
For appointments for examination / operation in Germany, Heidelberg University Hospital, please call: +49 - (0)6221-56 6283 (Secr. Pediatric Surg. Department Heidelberg). Please send me an email afterwards with the fixed date.
Austria: Prof. Hadidi examines patients and operates in Vienna.
Switzerland, Italy and Greece: Prof. Hadidi examines patients and operates also in these countries.
Please send an email for further information.
1. Is it possible to diagnose hypospadias during pregnancy and is that an indication for abortion?
2. I have already a child with hypospadias. How high are the chances that also the second child will be born with hypospadias?
3. What is the incidence of hypospadias?
4. When should we seek medical advice?
5. Which specialist should we contact? A pediatric surgeon, urologist or plastic surgeon?
6. How can I identify the severity of hypospadias of my child?
7. Is an operation necessary?
8. Will my son become normal after hypospadias-operation?
9. Will he function as a "normal" man later on when he grows up?
11. Should we do chromosomal analysis (tests)?
12. When should the hypospadias-operation be performed?
13. Which techniques are preferred for hypospadias-repair?
14. If the penis is curved, how would it be corrected and is this necessary?
15. How long does my child have to stay in hospital?
16. Does my child has to be bed ridden or can he move around after the hypospadias- operation?
17. How long should the dressing remain on the wound?
18. How long should the catheder remain in penis?
19. What is "Nesbit-Procedure" and when should it be performed?
20. What are the possible complications and how often do they occur?
1. Is it possible to diagnose hypospadias during pregnancy and is that an
indication for abortion?
Sometimes it is possible to diagnose hypospadias during pregnancy, but usually the diagnosis is only confirmed after birth. There is definitely no indication for abortion because of hypospadias.
2. I have already a child with hypospadias. How high are the chances that also
the second child will be born with hypospadias?
Usually hypospadias is sporadic. When one child has a hypospadias does not increase the chances of hypospadias for other children in the family. Rarely there are families where there may be genetic predisposition thats to say, the father, uncle or grandfather had hypospadias and in these rare instances more than one child can be affected.
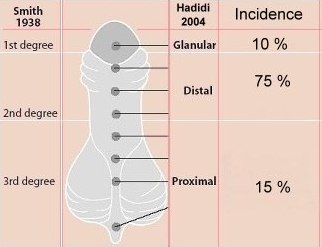
3. What is the incidence of hypospadias?
One in 125 boys to one in 300 boys has hypospadias.
In the United States a study reported that hypospadias was the most common congenital anomaly among whites. The incidence has been rising during the 1970s and 1980s.
 |
4. When should we seek medical advice?
Because the optimal window for hypospadias-correction is between 3 and 18 month it is ideal to seek the adivce of an experienced specialist during the first 3 month of life.
5. Which specialist should we contact? A pediatric surgeon, urologist or plastic
surgeon?
It is not important the speciality of the surgeon, what is more important is that he is interested in hypospadias and has large experience in hypospadias and has good results. In fact some of the world pionieers who have contributed a lot to the field of hypospadias were pediatric surgeons, others were urologists or plastic surgeons.
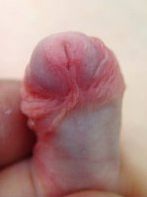
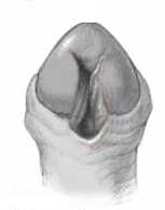
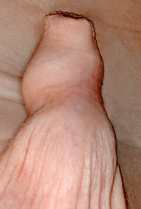
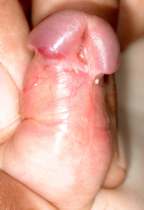
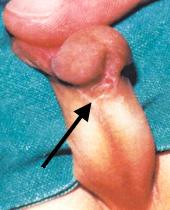
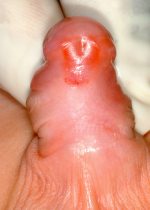
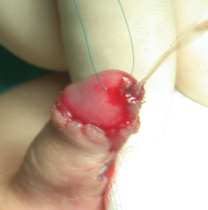
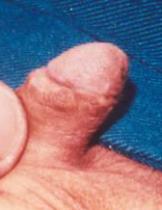
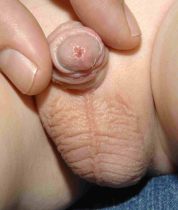
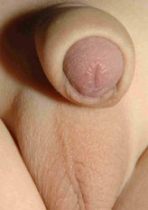
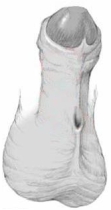
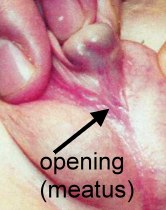
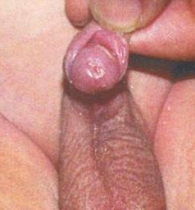
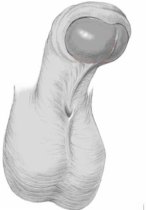
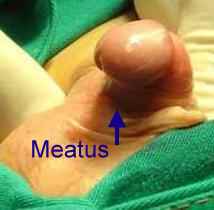
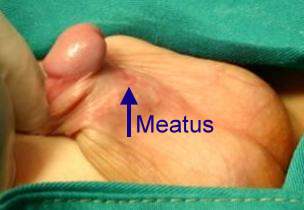
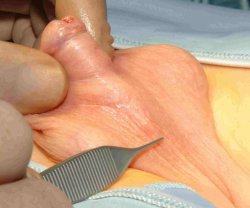
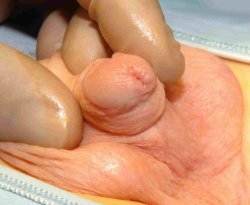
6. How can I identify the severity of hypospadias of my child?
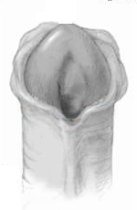
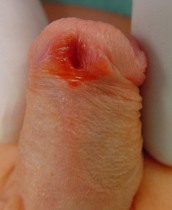
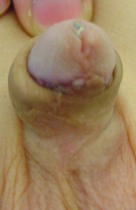
There are several factors that determines the severity of hypospadias. However as a general rule: if the opening is in the glance this is considered mild degree or grade 1. If the opening is in the outer half of the penis this is considered a moderate degree or grade 2. If the opening is in the inner half of the penis or in the scrotum, this is considered severe degree or grade 3. Please see examples below.
In reality the actual position of the meatus and the kind of the technique that is suitable for the child and the degree of curvature can not be accurately decided except in the operating theatre when the child is asleep.
Mild or moderate degrees of hypospadias constitute about 85 % of hypospadias. Severe forms constitute only 15 %.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7. Is an operation necessary?
If the child has a glanular hypospadias (grade 1) the operation may not be necessary from the functional point of view. This means that he may not have problems with urination or with erections and sexual function later on in life. However this mild form of hypospadias may affect the child psychologically as the penis will not look normal and may result in wetting his cloths during urination.
If the child has distal (grade 2) or proximal (grade 3) hypospadias the operation is important to ensure adequate functions of the penis in the form of urination, erection and sexual function later on in life. Apart from the repair, children with hypospadias may have a very narrow opening that needs to be widened or dilated in order to avoid back pressure and infection of the bladder and kidneys.
8. Will my son become "normal" after hypospadias-operation?
Yes, in children with glanular (grade1), distal (grade 2) and the majority of proximal (grade 3) hypospadias, if the operation is done by an experienced surgeon. However in a small percentage of patients (especially in proximal forms) complications may occur that may impair the appearance or the function of the penis.
9. Will he function as a "normal" man later on when he grows up?
In the majority of cases, yes.
10. Should my son receive hormonal treatment before the hypospadias-
operation?
Glanular and distal hypospadias and majority of proximal hypospadias do not need pre-operative hormonal treatment. Some surgeons prefer to use pre-operative hormonal treatment in the form of creme or injections in severe forms of proximal hypospadias. The drawback with hormonal treatment is that it does not affect the penis only but affects the whole body including bone growth and the effect of hormons on the penis is temporary (1 month after therapy).
Prof. Hadidi does not like to use pre-operative hormonal therapie because of its adverse effect on the body in general and because it alters the tissues of the penis and increases the chances of bleeding. However pre-operative hormonal therapy may be helpful in patients with intersex, where the phallus is very small.
11. Should we do chromosomal analysis (tests)?
In glanular and distal hypospadias this is not necessary. However in severe forms of proximal hypospadias or patients with intersex chromosomal tests are important to accurately identify the gender of the child.
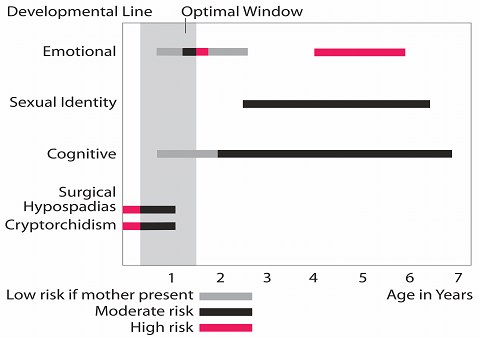
12. When should the hypospadias-operation be performed?
Recent studies showed that the ideal time for hypospadias correction is between 3 and 15 months as the penis grows less than 1 cm during the first 3 - 4 years.
 |