Frequently Asked Questions 13 - 20
(for individual questions please send an email)
13. Which techniques are preferred for hypospadias-repair?
14. If the penis is curved, how would it be corrected and is this necessary?
15. How long does my child have to stay in hospital?
16. Does my child has to be bed ridden or can he move around after the hypospadias- operation?
17. How long should the dressing remain on the wound?
18. How long should the catheder remain in penis?
19. What is "Nesbit-Procedure" and when should it be performed?
20. What are the possible complications and how often do they occur?
13. Which techniques are preferred for hypospadias-repair?
More than three hundred operations have been described for the treatment of hypospadias.
In general the popular techniques for glanular and distal hypospadias include the "Mathieu-" and "Tubularized Incised Plate Technique". For proximal hypospadias popular techniques include "lateral based flap", "onlay, "preputial island flap", "tubularized incised plate technique" and "two-stage-repair".
For glanular hypospadias with mobile meatus, the author prefers to use the "Inverted Y technique". For distal hypospadias, he prefers to use the "Y-V glanuloplasty modified Mathieu" approach. The author has adopted the "lateral-based flap technique"for proximal hypospadias.
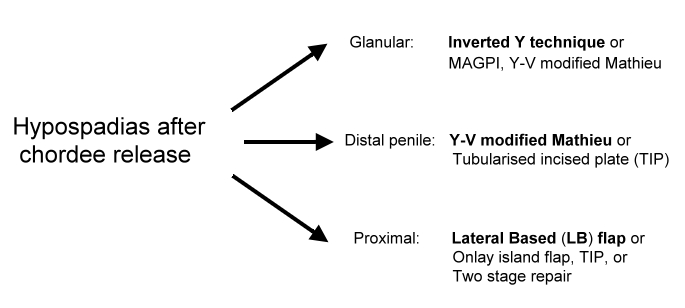 |
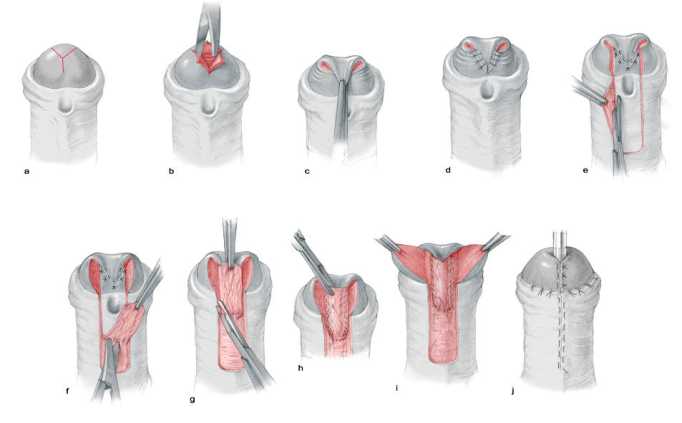 |
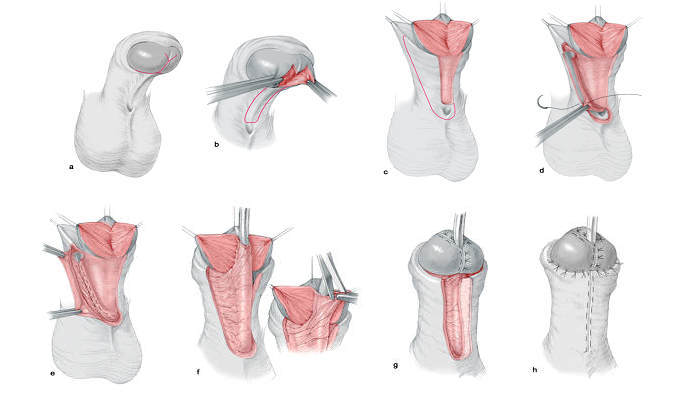 |
14. If the penis is curved, how would it be corrected and is this necessary?
Glanular hypospadias usually has no curvature at all.
80 % of distal hypospadias have no curvature as well. The remaining 20 % have curvature due to shortening of the skin that is usually corrected during the operation of hypospadias.
According to the experience of the author 80 % of the patients with proximal hypospadias have deep curvature that has to be corrected by excision of the fibrous unhealthy tissue that is usually present distal to the urethral opening.
15. How long does my child have to stay in hospital?
If the patient has glanular or distal hypospadias usually he can go home between 1 - 5 days after the operation depending on the age of the patient, the family circumstances and the degree of swelling after the surgery.
Children with proximal hypospadias need to have a catheder through the abdominal wall into the bladder for about 2 weeks. The child may stay in the hospital up to 2 weeks but may go home earlier if the mother can look after the child and ensure that the catheder does not come out.
16. Does my child has to be bed ridden or can he move around after the hypospadias-operation?
Usually the child is allowed to sit and move around and lead a normal life 24 hours after the operation (however care must be taken to protect the genital area).
However in proximal forms of hypospadias extra care must be taken to avoid slippage of the catheder outside the bladder.
17. How long should the dressing remain on the wound?
In glanular and distal forms the dressing is usually removed within 6 hours after the operation. In proximal the dressing is usually removed after 24 hours after the operation.
18. How long should the catheder remain in penis?
The author does not leave any catheders in the penis after operation because its his believe that the presence of catheder causes irratation and inflammation of the urethra and increases the chances of complications. So in cases of glanular and distal hypospadias the child is allowed to pass urine through the new urethra. In cases with proximal hypospadias the author inserts a catheder into the bladder through the abdominal wall and the catheder remains in place for 10 - 14 days.
19. What is "Nesbit-Procedure" and when should it be performed?
The "Nesbit-Procedure" is a procedure that tries to correct ventral curvature of the penis by shortening the upper surface of the penis. This usually results in further shortening of the penis.
The author does not recommend this approach for the correction of the penile curvature, as it results in shortening an already short penis.
20. What are the possible complications and how often do they occur?
The incidence of complications in glanular and distal hypospadias is less than 5 % if the operation is performed by an experienced surgeon.
The incidence of complications after proximal hypospadias is up to 20 % depending on the experience of the surgeon.
The commonest complication after hypospadias-surgery is fistula, which means that the urine comes from another opening in addition to the meatus. Other complications include infection, disruption of repair, meatal stenosis, loss of the flap, bleeding and disfigurement.
 |
 |
All the drawings were taken from the book "Hypospadias-Surgery, An illustrated guide", Springer 2004.